What is Cirrhosis?
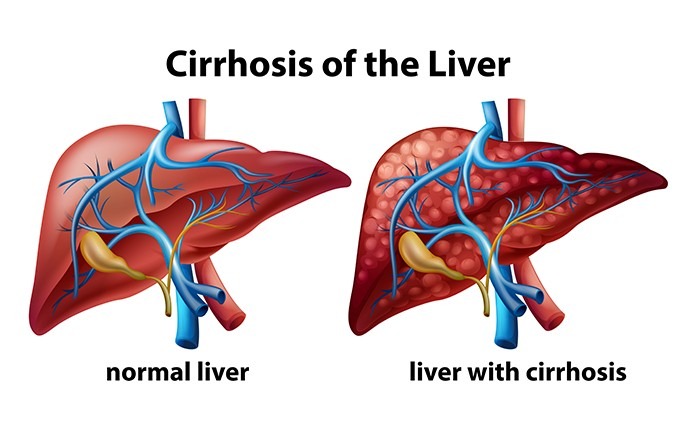
 Cirrhosis is a condition of the liver when it is scarred by a disease or another cause and its function gets impaired. There is incredible ability of the liver to repair itself but repeated insults lead to scarring. Even with scarring the liver may continue to function in a way to support normal life and life span of an individual provided the offending factors are removed (Compensated Cirrhosis) and it may stop its function suddenly, with no apparent cause at times (Decompensated Cirrhosis)
Cirrhosis is a condition of the liver when it is scarred by a disease or another cause and its function gets impaired. There is incredible ability of the liver to repair itself but repeated insults lead to scarring. Even with scarring the liver may continue to function in a way to support normal life and life span of an individual provided the offending factors are removed (Compensated Cirrhosis) and it may stop its function suddenly, with no apparent cause at times (Decompensated Cirrhosis)
Functions of liver: (Hard working organ doing hundreds of complex functions)
- Fighting infections and illness
- Regulating blood sugar
- Removing toxic substances from body
- Managing cholesterol levels
- Helping blood to clot
- Helps in digestion (particularly fats) with bile.
Causes of cirrhosis :
A – Alcohol
B – Hepatitis B
C – Hepatitis C
D – Diabetes, Drugs, including some that are used over the counter.
Other causes – eg. Obesity, Inadvertent clot formation in blood vessels of liver circulation, Auto immune (body’s immunity starts fighting against an organ like liver in one’s own body, disturbance with copper or iron stores in body, deficiency of a particular enzyme (alpha 1 trypsin) etc.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis:
Cirrhosis is a condition which is diagnosed incidentally in majority of the patients and can be a silent disease.
- Sometimes a patient can present with,
- Swelling and fluid in the tummy, legs and even lungs.
- Shortness of breath
- Bleeding from the swollen blood vessels from the food pipe which can be a life threatening condition. Also, easy bleeding or bruising in other areas of the body.
- Feeling tired and fullness of the tummy.
- Trouble getting to sleep or sleeping too much
- Yellow discolouration of the white of the eye and skin (Jaundice)
- Confusion that can come suddenly and even coma.
Cirrhosis impairs a one’s immunity and makes one more prone to infections. It also increases the risk of liver cancer.
Tests for Cirrhosis :
As mentioned before, Cirrhosis can be diagnosed incidentally without any symptoms in early stages by a simple ultrasound scan and at other times needs several tests to confirm the diagnosis, which are then needed to be put together and deciphered.
There are several tests which usually have to be done to find out the cause of Cirrhosis. It should never be assumed that there is only one cause of the damage to the liver as frequently we get patients with multifactorial damage to this organ.
Tests include blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT scan and MRI scan – sometimes all of them to clarify a cause of jaundice and confirm Cirrhosis. A specialised test called Liver Biopsy (taking a small piece of liver through a spring-loaded needle) can be recommended to clarify things.
How to prevent liver damage?
- Avoid alcohol.
- Do not take any medicine ‘over the counter’ including painkillers (eg. Ibuprofen, naproxen and even paracetamol) as indiscriminate use of these medicines and many others can cause serious damage to the liver.
- Do not use any herbal medication (including things like Liv 52) or supplements without checking with your doctor as these can cause liver damage too.
- Get vaccinated for Hepatitis (A and B viruses can be prevented) if indicated after checking with your doctor.
Treatment of Cirrhosis :
(Aim should be prevention, as it is an irreversible process) – Treatment of Cirrhosis falls in following categories:
Treat the cause
- Stop alcohol,
- Treat hepatitis,
- Stop the offending medicine, etc.
This may slow the process although overall damage is irreversible.
Treat the symptoms and signs of Cirrhosis– lower the risk of bleeding,
Once diagnosed with Cirrhosis, it is important to check the food pipe for swollen blood vessels by doing an endoscopy routinely. Following this one can be given medication as necessary to reduce the risk of bleeding. At times endoscopy has to be done to treat the bleeding by putting injections or rubber bands in the swollen areas (life threatening complication).
These measures aim at prolonging the life and improving its quality. Cirrhosis itself remains an irreversible process and may continue to cause complications and follow up is the key to treat complications.
Decrease the fluid build up
Once diagnosed with fluid in the tummy, a diagnostic tap of this fluid has to be done to confirm diagnosis and risk stratify an individual. Then medicines can be used to treat and sometimes we may need draining the fluid repeatedly or some special procedures may be helpful. However, these procedures are not free from related complications.
Treat and prevent infections :
Cirrhosis weakens the immune system and a patient not only becomes more susceptible but also has a tendency to get much sicker than someone without cirrhosis. This predisposes other organs of the body especially kidneys to damage as well. Hence, the treatment strategy is usually more aggressive, prolonged and with variable outcomes.
Treat confusion (encephalopathy – when brain gets affected by the toxins which can no longer be cleared by a damaged liver.)
Advanced liver disease can lead to confusion or coma. Certain antibiotics and agents which can soften the stool and clear or reduce ammonia in the process, can be helpful. Outcomes in such a situation can be unpredictable.
Liver Transplant or need for a new liver :
There is a need for a new liver in end stage patients. However, being on regular follow up this eventuality should be discussed with a doctor in advance to understand what this involves.
Liver transplant is never planned in an emergency situation but sometimes it may be worth being treated at a centre, short of the actual liver transplant, keeping their extensive experience for such situationin mind.
Prevent Cirrhosis
Are you a high risk individual? (see causes of Cirrhosis – A,B,C,D)
If yes, please identify your risk factor and see the doctor for tests.
Ask about Hepatitis Vaccination.
Please do not share needles, tooth brushes, use condoms for protection.
Be vigilant and go to standardised places for Dental (tooth) problems and medical & surgical procedures.